What Is a Rigid Flex PCB?
What Is a Rigid Flex PCB?
Blog Article
Rigid flex PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) combine the best features of both rigid and flexible PCBs. These hybrid circuit boards are designed to meet the needs of modern electronics, offering flexibility in areas that require bending while maintaining rigidity for components that need stability. In this article, we will explore what rigid flex PCBs are, how they are made, and why they are widely used.
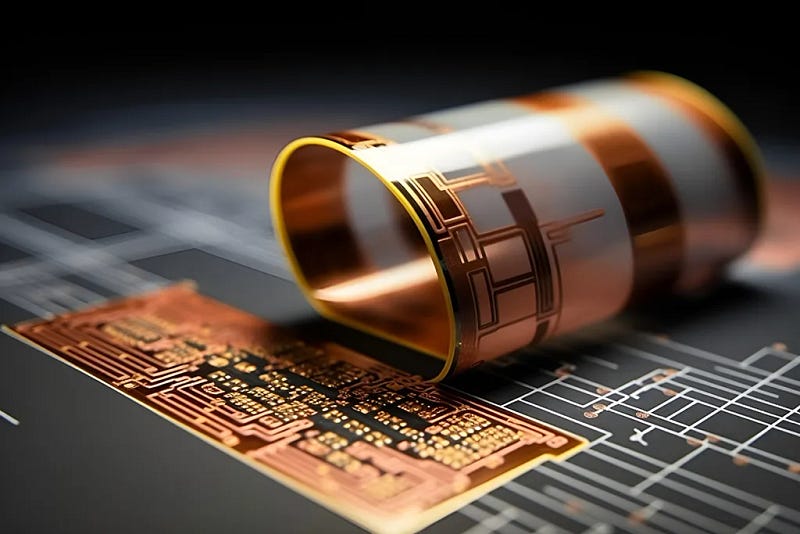
1. Structure of Rigid Flex PCBs
Rigid flex PCBs consist of both flexible and rigid sections. The flexible parts allow for bending, twisting, and folding, while the rigid sections provide a solid base for mounting components. Manufacturers layer these materials to create a board that can maintain structural integrity while also adapting to compact and irregularly shaped spaces.
The flexible portion is usually made from materials like polyimide, known for its high durability and flexibility. The rigid part is typically composed of standard FR4 or similar materials, which provide the necessary support for components that require a stable platform. This combination offers design flexibility without sacrificing performance.
2. How Rigid Flex PCBs Are Manufactured
Manufacturing rigid flex PCBs involves combining both flexible and rigid layers during the production process. First, manufacturers create the flexible part by applying copper layers on a flexible substrate, like polyimide. Then, they bond these flexible layers with rigid layers made of FR4 material.
The production process is more complex compared to standard PCBs. It involves multiple steps, including drilling, plating, and etching. However, this complexity allows manufacturers to create a versatile product that meets the requirements of different applications. The result is a circuit board that combines the strengths of both flexible and rigid designs.
3. Advantages of Rigid Flex PCBs
Rigid flex PCBs offer several advantages over standard PCBs. First, they provide excellent space efficiency. The flexible sections can be bent and folded to fit into small or irregularly shaped spaces, which is especially useful in compact electronic devices like smartphones and medical equipment.
Additionally, rigid flex PCBs improve reliability. By reducing the number of connectors and solder joints, they decrease the chances of mechanical failure. The rigid sections support components that require stability, while the flexible sections allow for movement, making these boards ideal for applications where both strength and flexibility are needed.
Moreover, rigid flex PCBs simplify assembly. They can be folded into their final shape, reducing the need for additional cables or connectors. This reduction in parts simplifies the assembly process and increases overall product reliability.
4. Applications of Rigid Flex PCBs
Rigid flex PCBs are widely used in various industries, particularly in applications where space and weight are critical factors. They are commonly found in:
- Consumer Electronics: Devices like smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology rely on rigid flex PCBs for their compact designs. The ability to fold and fit into tight spaces makes these boards ideal for sleek, lightweight devices.
- Medical Devices: Rigid flex PCBs are used in medical equipment, including pacemakers and hearing aids. Their flexibility allows for compact designs, while the rigid sections provide the stability needed for reliable performance in life-saving devices.
- Aerospace and Defense: In the aerospace industry, weight and reliability are crucial. Rigid flex PCBs help reduce weight while maintaining durability, making them suitable for aircraft, satellites, and military applications.
- Automotive Industry: Rigid flex PCBs are used in automotive electronics, such as infotainment systems, sensors, and control units. Their ability to withstand harsh environments and vibrations makes them ideal for automotive applications.
5. Challenges in Using Rigid Flex PCBs
Despite their many advantages, rigid flex PCBs come with challenges. The manufacturing process is more complex, leading to higher production costs. Additionally, design considerations must account for both the rigid and flexible sections, which requires expertise in layout and materials.
Moreover, testing rigid flex PCBs can be more complicated than testing traditional PCBs due to their hybrid nature. However, these challenges are outweighed by the benefits they bring to modern electronic designs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rigid flex PCBs offer a unique combination of flexibility and durability. Their hybrid design makes them ideal for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to aerospace and automotive industries. While they come with manufacturing complexities and higher costs, the advantages of space efficiency, reliability, and simplified assembly make them a popular choice in today’s advanced electronic products. As technology continues to evolve, rigid flex PCBs will play an increasingly important role in enabling compact, reliable, and high-performance devices.
Report this page